How to remove a web page from Google's index
Removing an existing URL from Google's index is known as deindexing. In this article, I'll cover how to remove a current URL from Google's search engine and avoid future URLs appearing, which is where most people go wrong.
Tl;dr - Cleaning up your website's Google search results
- Google's search engine results index is a database of millions of web pages.
- Google's algorithm returns the most relevant results when you search.
- Sometimes you want to avoid a URL appearing in search results or remove one that already does.
- Reasons to deindex a URL or domain from Google include duplicate content, development/testing versions of your URLs or domain, private web pages, and outdated content.
- To remove a URL from Google's search results, use Google Search Console and follow the step-by-step guide provided.
- You must check your robots.txt file and remove any disallow instructions before proceeding to the next stage.
- To stop URLs or domains from appearing in Google's search results, add a noindex tag to the header of the page(s) you want to remove.
Google's search engine results index is a database of millions of web pages from which, over time, Google's search bots have crawled and gathered information.
When you perform a Google search, the search engine trawls through its index and returns what it believes to be the most relevant results based on an algorithm of factors.
In most cases, website owners want their web pages to appear in Google's search results to help drive traffic to their websites. However, there are cases where you want to avoid a URL appearing in search results or remove one that already does. I've shared some examples of why you'd do this below.
I recently performed the task of removing URLs from Google for our website and was surprised at how difficult it was to find the correct process. Based on my experiences I created this guide to deindexing URLs from Google's index and how to avoid future indexing of URLs that create unwanted search results.
On this page
Why would you need to deindex a URL or domain from Google?
As a website owner, there are many reasons why you would want to avoid a web page appearing in Google. Here are just a few.
Duplicate content
If two pages contain very similar content, you can use canonical URLs to solve the issue. However, one of the pages aims to run a Google Adwords campaign that reuses existing site content. In that case, you should display it differently than the organic search results. This could result in the page being considered duplicate content. In most cases, Google Adwords landing pages are designed to generate conversions. They may have a different styling than the rest of the website.
Development/testing versions of your URLs or domain
Suppose the URL in question is for your website's preview or development version. In that case, you want to avoid development versions appearing as a search result in Google alongside your live website.
Private web pages
Pages you only want a user to see once logged in should be kept from Google.
Outdated content
You may have content that needs updating but don't have time to do it now. You could remove the web page from your website or request Google deindex the page temporarily.
Subscribe to our newsletter
How to remove a URL or domain from Google's index
To remove a URL from Google's search results, follow the step-by-step guide below. This process will temporarily remove the URL from Google's index for six months. You must follow the next stage – stopping URLs or domains from appearing in Google's index – to ensure that when the temporary URL removal request is lifted, Google doesn't reindex the URL.
Step 1) Create a list of the URLs or domains you want to remove from Google's index.
Step 2) Go to your Google Search Console account and sign in – https://search.google.com/search-console/
If you are a site owner and do not have a Google Search Console account, you can create one from the link above. It will ask you to add a property to your search console. For guidance, see how to add a Google Search Console property.
Step 3) Select the property that contains the URL you want to remove from Google's index. You may have multiple properties. For example, you may have properties for each subdomain or domain version – https://www, http://www, no http/s, or no www. The property you need is the one that matches the URL that you want to remove from Google. Click that link and look at which domain version that URL is on.
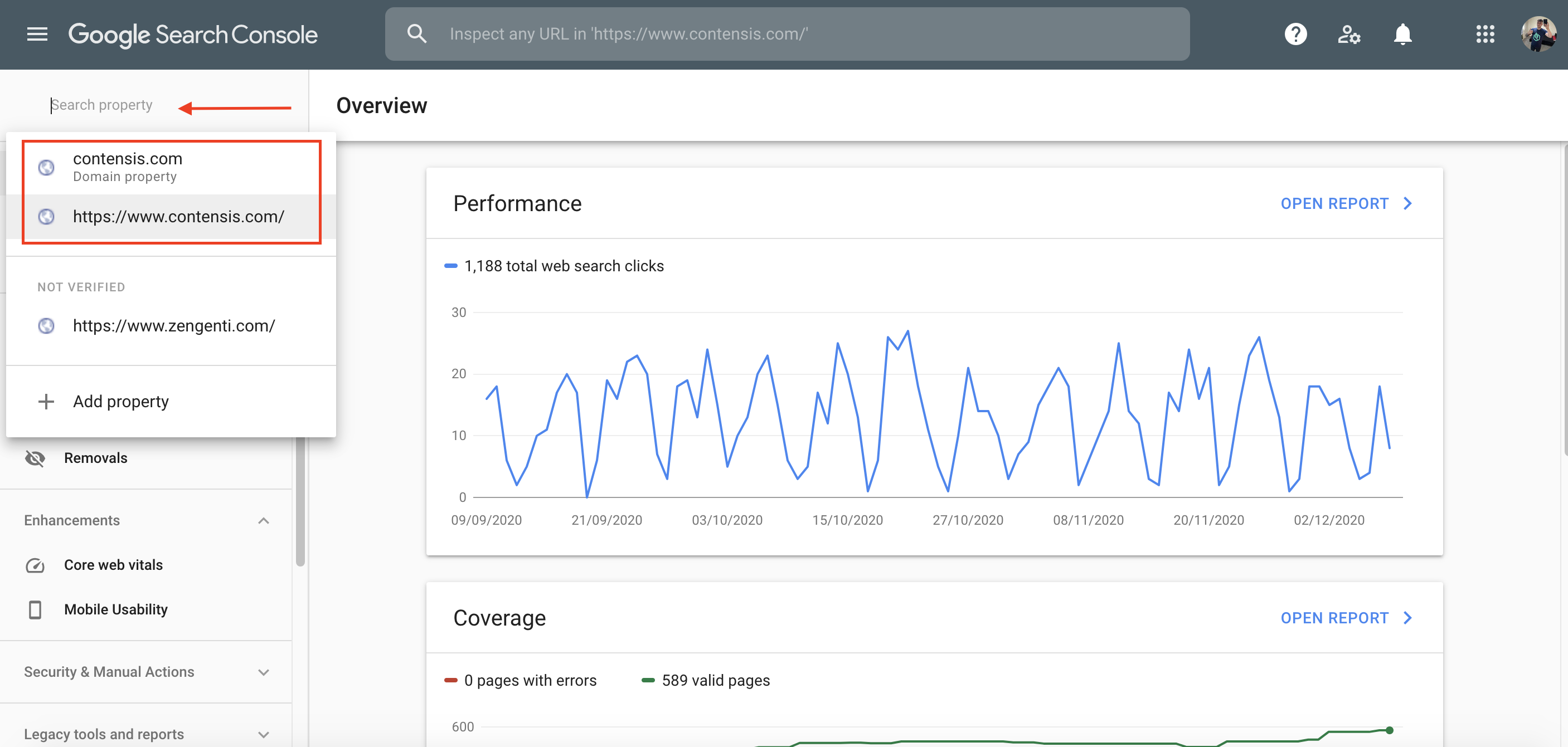
Step 4) Click Removals from the left-hand menu.
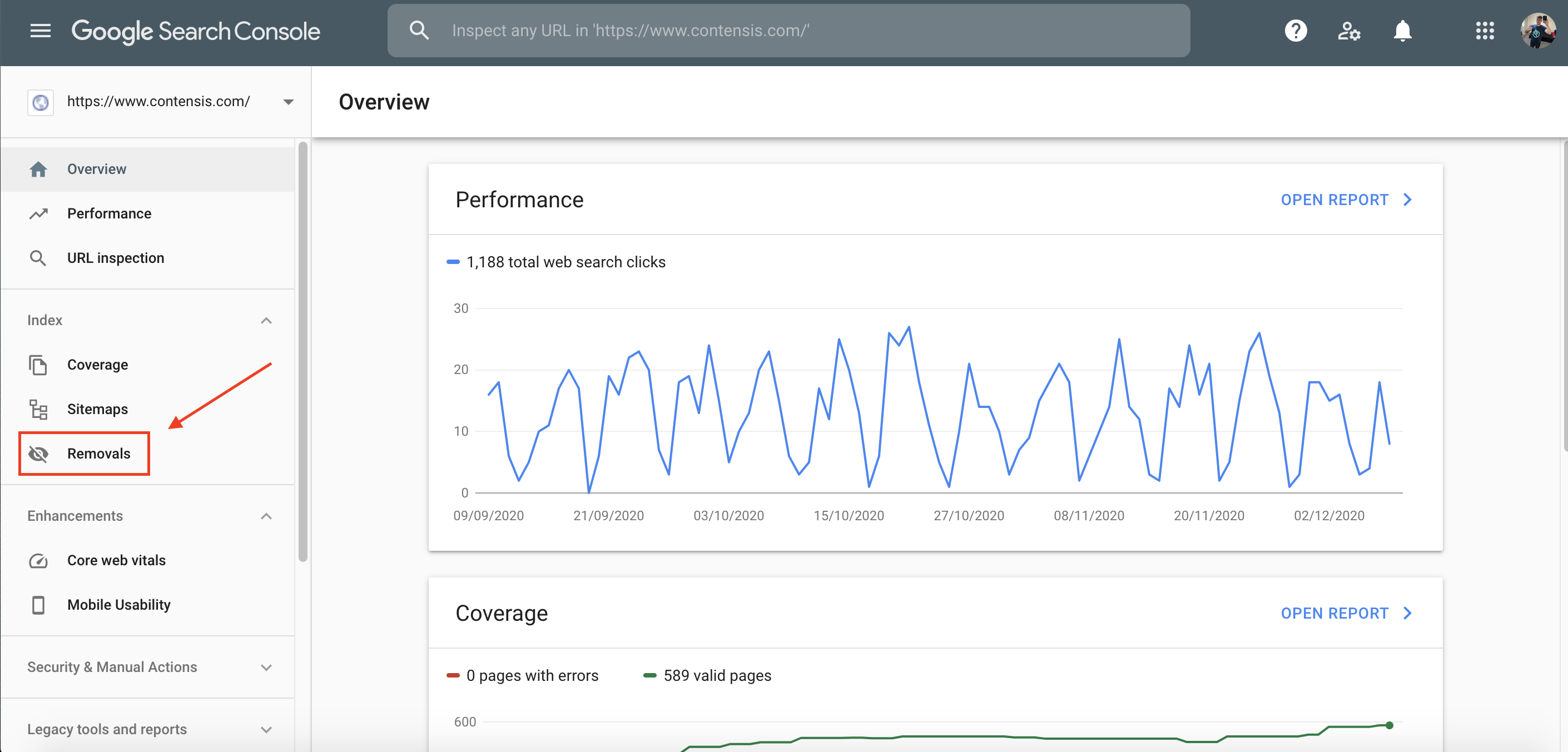
Step 5) Click the red button labelled New Request.
Step 6) Enter the full URL (including http/s and www if required – depending on your chosen property).
Step 7) If you only want to remove the URL, choose Remove this URL. If you want to remove the root domain and every URL within it, select Remove all URLs with this prefix. Only enter the root domain, not a full URL path for an internal page. For example, I'd enter https://www.contensis.com if I wanted to remove all URLs on this domain. I'd enter https://www.contensis.com/product/features to remove just this URL.
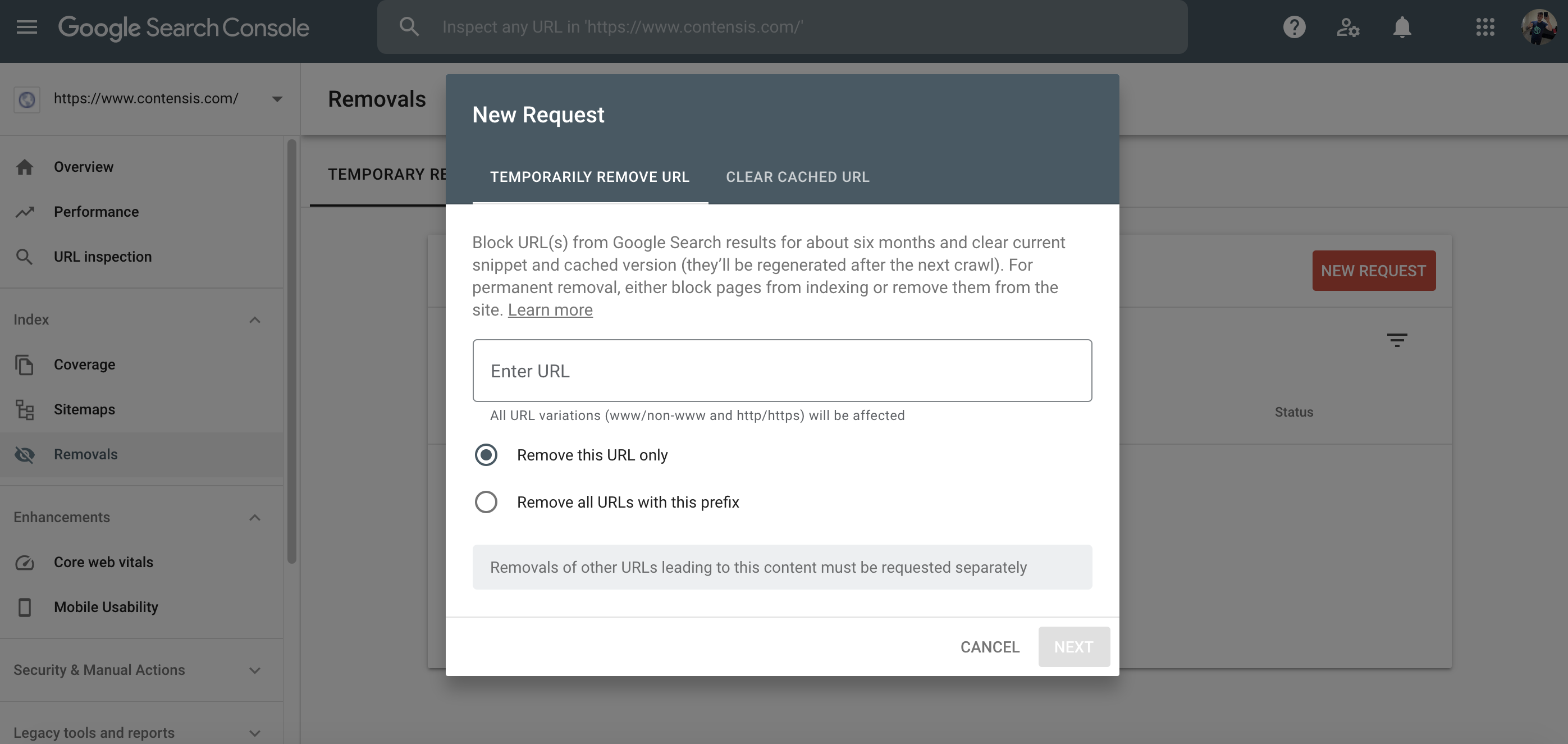
Step 8) Click Next.
Disclaimer: This request is temporary. Google will remove the URL from its search index now, but after six months, it will be able to reindex the URL. Therefore, it is vitally important that you move straight to the next stage below.
How to stop URLs or domains from appearing in Google's search results
Before you do anything
Before doing anything else, you must check your robots.txt file to ensure that you are not already blocking Google from crawling the URL. If you are, you need to remove this. This may sound odd; however, if Google cannot crawl your website, it cannot find the new noindex tag you will place in the header of a particular page. This tag will tell Google not to index the page (more on this later).
I have a disallow instruction in my robots.txt, so why has Google still indexed some of my URLs?
A common misconception is that you can instruct Google not to index your URLs by adding a disallow instruction in your robots.txt file. This only works sometimes. If this is the only place you have the instruction, you are likely to find you do have some URLs indexed by Google. In most cases, you can find your robots.txt file by adding /robots.txt to the end of your domain. Ask your web developer to locate the file if you cannot find it here.
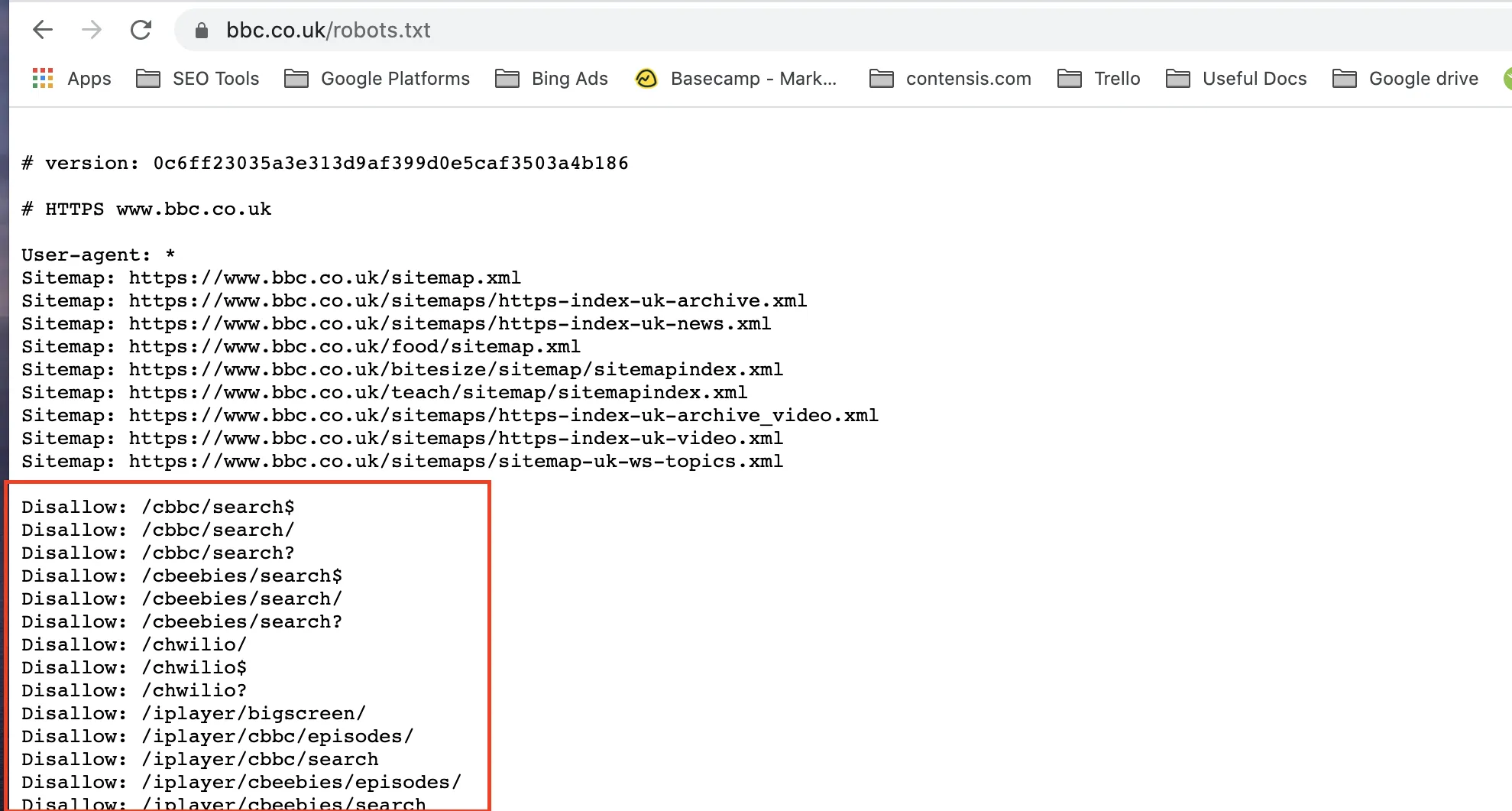
There are two ways in which Google can find a website URL. The first is submitting your sitemap to Google through the search console or requesting an index of a particular URL. The second is when Google follows a link from another website to yours. When Google takes the latter path to your website, it won't always see your robots.txt file to know which URL you do not want it to index. This is the cause for most of the issues people have faced when finding URLs in Google's index that shouldn't be there.
To confirm this, the following statement is from the robots.txt FAQ section in Google's Search Central guidelines and help documentation:
If I block Google from crawling a page using a robots.txt disallow directive, will it disappear from search results?
Blocking Google from crawling a page will likely remove the page from Google's index.
However, robots.txt Disallow does not guarantee that a page will not appear in results: Google may still decide, based on external information such as incoming links, that it is relevant. If you wish to explicitly block a page from being indexed, use the noindex robots meta tag or X-Robots-Tag HTTP header instead. In this case, you should not disallow the page in robots.txt because the page must be crawled for the tag to be seen and obeyed.
How to correctly request a noindex from Google
You need to do two things to request a noindex from Google. First, you need to ensure that you are not using a disallow instruction for this URL in your robots.txt file already. Check carefully because you may be disallowing a whole folder in which the URL is located. The second thing you need to do is add a specific tag.
To correctly request a noindex from Google or other search engines, you must do one of the following as part of the removal process.
Add a meta robots tag
Place this in your URL's <head> section – the page you do not want Google to index.
Add X-Robots-Tag HTTP header
This can be used as an element of a URL's HTTP header response.
For complete and current instructions on how to add these tags and what to include, see Google's Robots meta tag, data-nosnippet, and X-Robots-Tag specifications.
Which method should I use?
The following is a quote from Google and can again be found in Google's Search Central documentation
- robots.txt: Use it if crawling of your content is causing issues on your server. For example, disallow crawling of infinite calendar scripts. You should not use the robots.txt to block private content (use server-side authentication instead) or handle canonicalization. If you must be sure that a URL is not indexed, use the robots meta tag or X-Robots-Tag HTTP header instead.
- robots meta tag: Use it to control how an individual HTML page is shown in search results (or to ensure it's not shown).
- X-Robots-Tag HTTP header: Use it to control how non-HTML content is shown in search results (or to ensure it's not shown).
Final reminder
If you have removed a disallow from your robots.txt for Google to see your new noindex tag, you should return it afterwards. As soon as you see Google has removed your URL from its search results (you may have to check this manually in Google search), put your disallow instruction back into your robots.txt file if required.







