How to optimise content for AI-assisted search
The evolution of generative AI, particularly in tools like ChatGPT and Google's Search Generative Experience (SGE), is transforming how users discover and interact with digital content. Editors need to optimise their content for these emerging AI search engines and adapt their workflows to stay relevant.
Harnessing Google's SGE and AI-powered search engine capabilities
Google's Search Generative Experience ecosystem is part of a new class of AI-powered search engines that aim to provide smarter, more contextual answers. Features like conversational search through smart devices and AI-generated answers offer condensed responses and suggested follow-up questions.
This shift has contributed to a sharp rise in no click searches, where users find what they need without visiting the source website.
How to optimise content for AI search engines
A typical article, like one on “The Benefits of Remote Work,” should be structured with AI search optimisation in mind:
- Start with a clear overview: Highlight key points up front (e.g. flexibility, productivity, cost savings).
- Use question-led subheadings: Mimic user queries such as "How does remote work improve productivity?"
- Provide actionable takeaways: Add a closing section like "Top AI tools for remote collaboration".
This approach reflects what Google's EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) guidelines prioritise – useful, quality content that performs well in both traditional search engines and newer AI search platforms.
This structure might not look much different from how you write content now. If this is the case, that means you're focusing on writing quality and engaging articles. The main difference is in the expected rise of conversational-style writing along the lines of the dreaded "FAQ" section.
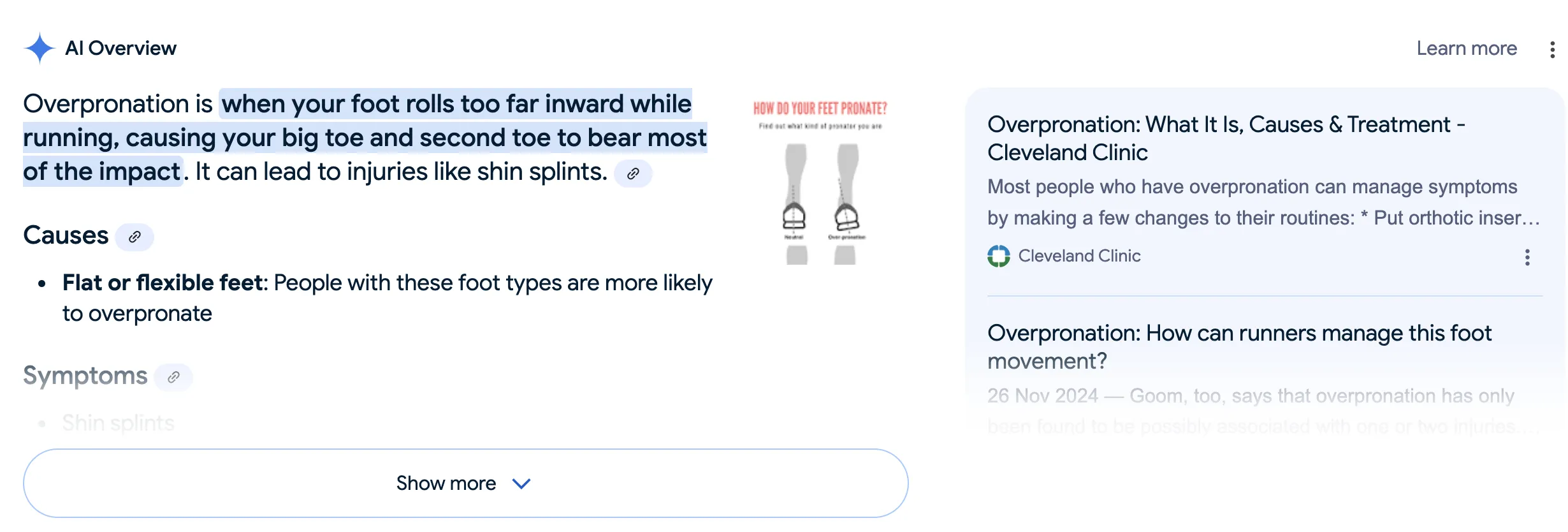
Structuring your articles for AI discovery
To make your content more accessible to generative AI search engines, follow these steps:
Answer the query upfront
Begin with a direct response to the likely search question. For example, “How to Choose the Right Running Shoes” should start with the key decision factors: fit, material, surface type.
Use natural language and question-based subheadings
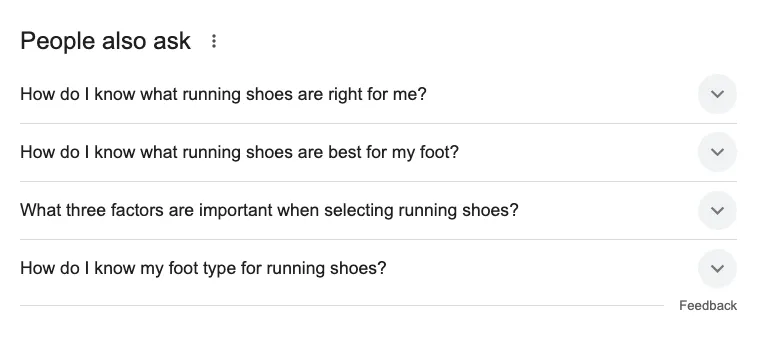
Incorporate phrases from tools like Google’s “People Also Ask”. Example queries:
- “What should you consider when buying running shoes?”
- “What are the best running shoes for trail running?”
- “How do I know my foot type?”
These long-tail keywords help content rank in AI search engines and traditional SEO contexts.
Add scannable elements
AI models – and users – favour clarity. Use:
- Bullet points
- Comparison tables
- Infographics (with alt text for accessibility)
A tool like Insytful can help you meet these accessibility requirements while optimising for both AI engines and user experience.
Include related follow-up content
Anticipate what users might want to learn next. When creating an article, I will usually add an FAQ section after the concluding paragraph to answer queries I've found in Google's related search sections. This trend is continuing with conversational AI-assisted searches.
Keep users engaged by adding sections like:
- "How to care for your running shoes to make them last longer."
- "Running shoes cushioning types."
- "Important of proper running form."
These also target related AI search results.
Optimising for both Google and AI search platforms
Use conversational, intent-rich keywords
Naturally include terms like:
- “How to reduce foot pain from running”
- “Best running shoes for beginners”
- “AI tools for improving fitness habits”
These long-form keywords align with the language patterns used by NLP-based AI search engines, helping you surface in AI-generated answers.
Use structured data
Add schema markup to your articles for FAQs, reviews, and how-to sections. This improves visibility in features like snippets and AI search overviews. Many platforms, like WordPress, will do this out of the box, but others will require some development work to add these schemas to your pages' markup.
Here’s an example of a basic schema markup for an article about the best running shoes. This is written in JSON-LD format, which is widely used for structured data:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "The Best Running Shoes for 2025",
"description": "A comprehensive guide to the top running shoes for all types of runners, including reviews and recommendations.",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Jane Doe"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Running World",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://www.runningworld.com/logo.png"
}
},
"datePublished": "2025-01-15",
"dateModified": "2025-01-18",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.runningworld.com/best-running-shoes-2025"
},
"image": [
"https://www.runningworld.com/images/best-running-shoes-1.jpg",
"https://www.runningworld.com/images/best-running-shoes-2.jpg"
],
"articleSection": "Running Gear Reviews",
"keywords": "running shoes, best running shoes 2025, top running gear",
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.8",
"reviewCount": "120"
}
}
</script>
Include links to authoritative sources
Google's Search Generative Experience and ChatGPT prioritise content that demonstrates expertise and credibility.
To build trust and authority:
- Cite reliable sources: Link to studies, reports, and statistics from trusted organisations or academic institutions. For example, referencing a study on running shoe performance from a respected sports science journal adds weight to your claims.
- Use data to back up your points: Include useful metrics or benchmarks. Instead of saying, "These shoes are lightweight," specify, "At only 250 grams, these shoes are 15% lighter than the average running shoe, according to [Source]."
- Partner with authoritative sites: Aim to have your content referenced or linked by high-quality, credible websites. This could involve collaborating with industry blogs, universities, or recognised experts. For instance, sharing your guide with organisations like the British Journal of Sports Medicine could encourage valuable backlinks, boosting your domain rating and article visibility in search.
Keeping content fresh and relevant
AI models like those used Google's Search Generative Experience prioritise content that is not only up-to-date but also relevant and insightful. To make your content stand out, it's important to go beyond updating the publication year. Refresh your material with updates that reflect current developments, tools, and best practice.
For example, an older article on "Digital Marketing Strategies" can be revised to include the latest data, case studies, and cutting-edge tools, such as AI-driven platforms for campaign management. Trends like the rising popularity of platforms such as TikTok or Snapchat for AI search among Gen Z can provide valuable context and keep the content relevant to the audience.
Outdated recommendations should be re-evaluated and replaced with alternatives that reflect the industry's current state. By consistently revising content, you establish your work as reliable and forward-thinking, meeting the standards that both AI engines and human readers appreciate.
The future of AI-assisted search
Google's Search Generative Experience, ChatGPT search, and other AI search engines are changing how people find and interact with information.
To stay visible:
- Optimise for AI search results
- Use structured content
- Focus on helpful, conversational language
By aligning with both AI search optimisation best practice and traditional SEO standards, you'll be well-placed to serve your audience—whether they arrive through a click or never leave the search results at all.







